Trade wars and protectionism have surged into the spotlight, stirring the pot of global economics. These strategies, involving tariffs and regulatory policies, aim to enhance domestic growth but often ripple through international markets, unsettling everything from trade balances to diplomatic ties.
The Rise of Trade Wars
Trade wars often begin as attempts to defend local businesses from international competitors. Recent years have seen the U.S. initiating tariffs on powerhouse economies like China, Canada, and Mexico, purportedly to rebalance trade deficits and protect domestic industries.
Historical Context and Initiating Factors
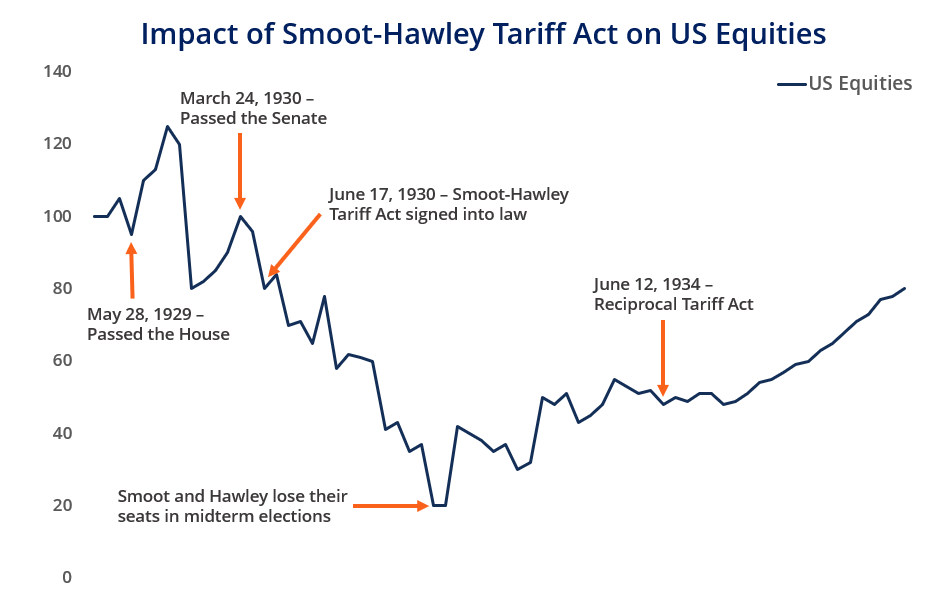
This isn’t the first time the world has seen such economic skirmishing. Trade disputes have historical roots, from the Smoot-Hawley Tariff of the 1930s to more recent altercations like those between the U.S. and China. These confrontations are often fueled by desires to safeguard local employment and industry from foreign competition. The 2018-2019 U.S.-China trade war illustrated how such measures can affect hundreds of billions in trade.
Key Players in the Global Trade Conflict

Today, the U.S., China, Canada, and Mexico stand at the center of this economic tug-of-war. For America, it’s about tackling trade deficits. Canada and Mexico, meanwhile, deal with their extensive reliance on U.S. markets. China faces its own challenges, maneuvering its massive export economy to weather U.S. import tariffs.
Impact of Protectionism on Global Economies

Protectionist policies inevitably lead to global ripple effects, influencing everything from macroeconomic stability to individual consumer habits.
Effects on U.S. Economy
In the U.S., imposed tariffs have increased costs for both industries and consumers, leading to higher prices and stifling competition. According to economic analysis, these measures often fail to deliver on promises of job retention, as noted by economists. They can slow GDP growth, making the U.S. less competitive.
Repercussions for Canada and Mexico
For Canada and Mexico, the economic outlook is tinged with uncertainty. Trade barriers increase the financial burden on their export-driven sectors, leading to strained economic growth. The recent postponement of additional tariffs on these nations, as reported by recent updates, gave temporary relief but left underlying economic threats unaddressed.
Influence on China’s Economy
China, with its export-heavy economy, grapples with the regulatory burden imposed by U.S. tariffs. In response, it’s implementing strategies to diversify its trade portfolio and lessen dependency on the U.S. Despite being on the receiving end, China’s countermeasures include tariffs on select U.S. products, amplifying global trade tensions.
Shifts in Global Supply Chains
Trade wars naturally instigate shifts in how goods are produced and distributed globally.
Industries Most Affected
Industrial sectors, like manufacturing, technology, and automotive, have felt the brunt of supply chain disruptions. These sectors are struggling with the need to localize production or source alternative suppliers, a move that can increase costs and lead to delays.
Future Predictions for Supply Chain Management
Looking ahead, supply chain strategies may see a global overhaul. Companies could increasingly lean on technology for real-time tracking, diversify their supplier bases, and emphasize local production to mitigate risks from protectionist policies. International market insights suggest a recalibration of supply chain networks as businesses adjust to tariff implications and geopolitical uncertainties.
Geopolitical and Social Implications

Beyond the spreadsheets and economic forecasts, trade wars affect international relations and social well-being.
Impact on International Relations
Economic hostilities often bleed into diplomatic relations. Strained alliances and fractured ties are increasingly common as countries prioritize national interests over global cooperation. Tariff battles, as seen in the U.S. and Canada-Mexico relations, can foment uncertainty not just economically, but within international political dynamics.
Consumer and Labor Impacts
On the ground, everyday consumers face higher prices for goods, while industries grapple with layoffs and diminished competitiveness. Workers, particularly in vulnerable sectors like manufacturing, bear the brunt of shifting trade policies, resulting in job insecurity and stagnated wages.
Conclusion
Trade wars and protectionism continue to shape our economic landscape in 2025. While intended to bolster national industries, their side effects are far-reaching, from disrupting supply chains to altering international relations. As nations continue to navigate this complex milieu, an understanding of the long-term impacts remains crucial for policymakers and businesses alike. The evolving nature of global trade demands adaptability and foresight to minimize economic upheavals while maximizing growth opportunities.



